Ça-a-eté? Against Barthes
Joan Fontcuberta
15.10.2021 – 13.02.2022
-> Guided tours to Adrià Julià and Joan Fontcuberta
-> Guided tours to Guido Guidi and Joan Fontcuberta
Walter Benjamin aside, the most cited essay on photography in history is without a doubt Camera Lucida. It is Roland Barthes’ final book, and was published shortly before his death. With his poetic gaze and theoretical reflections, Barthes develops key concepts in the book, such as punctum and studium, which have since been incorporated into the heritage of photographic criticism. In one of the most significant passages, we find another central idea: “In Photography I can never deny that the thing has been there. There is a superimposition here: of reality, and of the past. And since this constraint exists only for Photography, we must consider it, by reduction, as the very essence, the noeme of Photography. What I intentionalize in a photograph is neither Art nor Communication, it is Reference, which is the founding order of Photography. Photography's noeme will therefore be: ‘That-has-been’” [Ça-a-été].
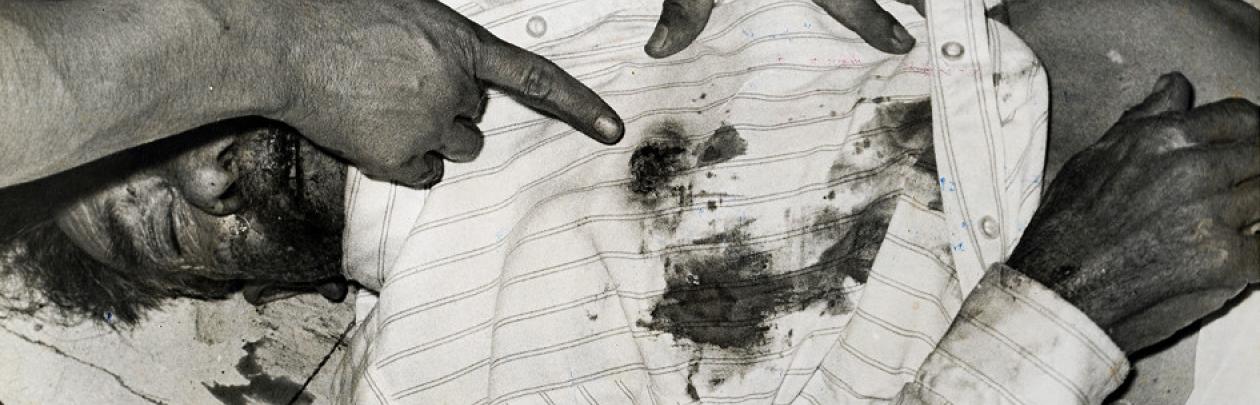
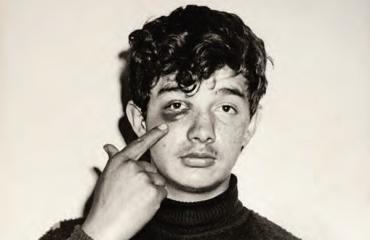
This ça-a-été constitutes the ontological bulwark of photography’s documentary value: without the certainty of “that-has-been”, all visual testimony ends up delegitimated. This is why it could be beneficial to analyse photo-journalistic snapshots in light of this criteria. For example, as a case study, we could take the photographic archive of the now-closed Mexican journal Alerta, a tabloid dedicated to blood and guts news stories, which in Latin America is referred to as “nota roja” [red note]. If we do an analysis, we are surprised to see how frequently the iconological pattern of the gesture of pointing appears: a figure in the image (a victim, a witness, an “expert”, whoever) points with a finger at someone or something in the composition to draw attention to it. These are theatrical, artificial situations where it is clear that the model is following the reporter’s instructions, while nevertheless making doubly clear the pretension of applying he principle of ça-a-été, in a way that is as naïve as it is rudimentary. We are witness to an effect of superimposed indexicalities: one passed down through photography and the other of the finger (the index) pointing. Both the camera lens and the finger focalise our perception towards something that has gone by. Yet the staging is so naïve, rudimentary and artificial that instead of emphasising, what it does is problematise the validating value of the camera, especially in genres like forensic and news photography, which should be characterised precisely by an aseptic, derhetorized treatment of information.
Barthes, perhaps, fascinated by the theatricality he had also dedicated enthusiastic studies to, sought to pass over this drift: “What is theatricality?”, he asked in 1971. “It is not decorating representation, it is unlimiting language.” Very well, then, but if so, ça-a-été is no longer a guarantee of objectivity, inasmuch as it explores staging. A triple staging, in fact, as all photography implies the staging of the object, the gaze and of the photographic device itself. It is from the conciliation of these stagings that language emerges. We can decide to not limit it, we can grant it all freedom available to it, but at the cost of breaking the contract of verisimilitude.
Unmasked by the overplayed gesticulation of accusing or pointing fingers, we discover that the noeme heralded by Barthes is more a theatrical operation than one of reference. “That has been”, indeed, but what, in fact, has really been? It is imperative to ask this when there is no spontaneity, but rather construction. Yet worst of all is that photography, in and of itself, tells us very little about “that”. Very little beyond scenery and costumes.
Joan Fontcuberta